-
University Guide
 University Guide
University Guide
INDEX- Introducing the President
- University Introduction
- University Evaluation
-
Policies and Initiatives
- Policy and Initiatives INDEX
- Compliance
- Crisis Management System
- Promoting gender equality
- International Exchange Policy
- Infrastructure longevity plan (individual construction plan)
- Environmental Initiatives
- Smoking is prohibited throughout the university grounds.
- Safety Management Action Plan
- JABEE Initiatives
- Basic rules regarding drinking among Muroran Institute of Technology students
- Policy for promoting the sharing of research facilities and equipment at Muroran Institute of Technology
- Campus Master Plan
- Muroran Institute of Technology Conflict of Interest Management Policy
- Digital Campus Promotion
- Muroran Institute of Technology Open Access Policy
- Muroran Institute of Technology Research Data Policy
-
Information Disclosure
- Information Disclosure INDEX
- Disclosure of corporate information (information about the organization)
- Disclosure of corporate information (information regarding business)
- Disclosure of corporate information (financial information)
- Publication of corporate information (evaluation information)
- Disclosure of corporate information (audit information)
- Publication of educational information
- Compliance status with the National University Corporation Governance Code
- Rules
- Information Disclosure System
- Personal Information Protection System
- Publication of guidelines for employees regarding the promotion of the elimination of discrimination against people with disabilities
- Announcement of the New Support System for Higher Education
- Application and recruitment information
- public relations
-
Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
 Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
INDEX- Faculty of Science and Engineering
- graduate school
-
Affiliated facilities (centers, etc.)
- Affiliated Facilities (Centers, etc.) INDEX
- Creative Collaboration Center
- Aerospace Plane Research Center
- Rare Earth Materials Research Center
- Computer Science Center
- Research Infrastructure Equipment Sharing Center
- Technology Department
- Career Support Center
- International Exchange Center
- Information Education Center
- Affiliated Library
- Health Management Center
- Gender Equality Promotion Office
- MONO Creation Future Co-Creation Organization
- Regional Collaboration Human Resources Development Center
- Manufacturing Infrastructure Center
- Robot Arena
- satellite
- Tokyo Office
- the study
-
Student Life/Employment
 Student Life/Employment
Student Life/Employment
INDEX-
Courses and classes
- Course/Class INDEX
- Academic Calendar
- Lesson plan (syllabus)
- Classes (timetable)
- Exam (timetable)
- Course Affiliation
- Credit transfer with other universities
- Re-reading of course subjects
- CAMPUS SQUARE (Course registration)
- How to take the course
- Student Handbook/Graduate School Course Guidelines
- Transfer of departments, etc.
- Doctoral Degree Application Guide
- Academic Counseling and Guidance
- Duration of study
- Long-term student system
- Educational Programs (not required for graduation or completion)
- A Note About Generative AI
-
Student Life
- Student Life INDEX
- Suspension and Absence
- Various notification and certificate issuance procedures
- Student ID and student number
- Student discount card/school attendance certificate
- Procedures for taking a leave of absence, reinstating, and withdrawing from school
- New academic year orientation
- Preserving the on-site environment
- Attention students
- Transportation on and off campus
- Message board/contact method
- Harassment
- health care
- Events
- Welfare facilities
- Student Dormitory
- Student Support Center Introduction
- Student General Advice Office
- Extracurricular Activities
- Tuition, scholarships and other procedures
- Employment and qualification support
-
Courses and classes
-
Entrance Examination Information
 Entrance Examination Information
Entrance Examination Information
INDEX- University Entrance Examination [Faculty]
- Graduate School Entrance Examination
- Transfer Admissions
- Entrance examination for international students
- Specialized students and research students
- Admission procedures, tuition fees, etc.
- FAQ
- University Introduction
- Request information

-
Social Cooperation
 Social Cooperation
Social Cooperation
INDEX- Collaborative News
- Collaboration Centers, etc.
-
Industry-academia-government collaboration
- Industry-academia-government collaboration INDEX
- Alliance Lab
- Research Collaboration Association
- Muro Institute of Technology venture title
- Confidentiality
- Joint Research System
- Commissioned Research System
- Academic Guidance System
- Tangible research results
- Scholarship and Donation System
- Donation field etc.
- Future Creation Promotion Expenses
- Regarding the expenditure of personnel expenses of the principal investigator (PI) from direct costs of competitive research grants
- Research ethics and safety
- Public Lectures
- Muro Institute of Technology Science School
- University Visit
- Robot Soccer Contest
- Re-education for working adults
-
International Exchange
 International Exchange
International Exchange
INDEX- International Academic Exchange Agreements
- Number of international students
- Researcher Database
- Entrance Exam
- Tuition Fees
- International Student Support (for new students)
-
Support for international students (for current students)
- Scholarships for International Students
- Japanese Language Course for International Students
- Immigration procedures (renewal of period of stay, permission to engage in activities other than those permitted under the status of residence, re-entry permission)
- Procedures after arriving in Japan
- Procedures for changing address (under construction)
- Procedures upon returning to Japan
- Notification of absence due to temporary return to Japan, travel, etc.
- Employment for international students
- Emergency Contact Information
- Studying abroad from Muro Institute of Technology
- Request for donations
-
University Guide
University Guide INDEX
- Introducing the President
- University Introduction
- University Evaluation
-
Policies and Initiatives
- Policy and Initiatives INDEX
- Compliance
- Crisis Management System
- Promoting gender equality
- International Exchange Policy
- Infrastructure longevity plan (individual construction plan)
- Environmental Initiatives
- Smoking is prohibited throughout the university grounds.
- Safety Management Action Plan
- JABEE Initiatives
- Basic rules regarding drinking among Muroran Institute of Technology students
- Policy for promoting the sharing of research facilities and equipment at Muroran Institute of Technology
- Campus Master Plan
- Muroran Institute of Technology Conflict of Interest Management Policy
- Digital Campus Promotion
- Muroran Institute of Technology Open Access Policy
- Muroran Institute of Technology Research Data Policy
-
Information Disclosure
- Information Disclosure INDEX
- Disclosure of corporate information (information about the organization)
- Disclosure of corporate information (information regarding business)
- Disclosure of corporate information (financial information)
- Publication of corporate information (evaluation information)
- Disclosure of corporate information (audit information)
- Publication of educational information
- Compliance status with the National University Corporation Governance Code
- Rules
- Information Disclosure System
- Personal Information Protection System
- Publication of guidelines for employees regarding the promotion of the elimination of discrimination against people with disabilities
- Announcement of the New Support System for Higher Education
- Application and recruitment information
- public relations
-
Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc. INDEX
- Faculty of Science and Engineering
- graduate school
-
Affiliated facilities (centers, etc.)
- Affiliated Facilities (Centers, etc.) INDEX
- Creative Collaboration Center
- Aerospace Plane Research Center
- Rare Earth Materials Research Center
- Computer Science Center
- Research Infrastructure Equipment Sharing Center
- Technology Department
- Career Support Center
- International Exchange Center
- Information Education Center
- Affiliated Library
- Health Management Center
- Gender Equality Promotion Office
- MONO Creation Future Co-Creation Organization
- Regional Collaboration Human Resources Development Center
- Manufacturing Infrastructure Center
- Robot Arena
- satellite
- Tokyo Office
- the study
-
Student Life/Employment
Student Life/Employment INDEX
-
Courses and classes
- Course/Class INDEX
- Academic Calendar
- Lesson plan (syllabus)
- Classes (timetable)
- Exam (timetable)
- Course Affiliation
- Credit transfer with other universities
- Re-reading of course subjects
- CAMPUS SQUARE (Course registration)
- How to take the course
- Student Handbook/Graduate School Course Guidelines
- Transfer of departments, etc.
- Doctoral Degree Application Guide
- Academic Counseling and Guidance
- Duration of study
- Long-term student system
- Educational Programs (not required for graduation or completion)
- A Note About Generative AI
-
Student Life
- Student Life INDEX
- Suspension and Absence
- Various notification and certificate issuance procedures
- Student ID and student number
- Student discount card/school attendance certificate
- Procedures for taking a leave of absence, reinstating, and withdrawing from school
- New academic year orientation
- Preserving the on-site environment
- Attention students
- Transportation on and off campus
- Message board/contact method
- Harassment
- health care
- Events
- Welfare facilities
- Student Dormitory
- Student Support Center Introduction
- Student General Advice Office
- Extracurricular Activities
- Tuition, scholarships and other procedures
- Employment and qualification support
-
Courses and classes
- Entrance Examination Information
-
Social Cooperation
Social Collaboration INDEX
- Collaborative News
- Collaboration Centers, etc.
-
Industry-academia-government collaboration
- Industry-academia-government collaboration INDEX
- Alliance Lab
- Research Collaboration Association
- Muro Institute of Technology venture title
- Confidentiality
- Joint Research System
- Commissioned Research System
- Academic Guidance System
- Tangible research results
- Scholarship and Donation System
- Donation field etc.
- Future Creation Promotion Expenses
- Regarding the expenditure of personnel expenses of the principal investigator (PI) from direct costs of competitive research grants
- Research ethics and safety
- Public Lectures
- Muro Institute of Technology Science School
- University Visit
- Robot Soccer Contest
- Re-education for working adults
-
International Exchange
International Exchange Index
- International Academic Exchange Agreements
- Number of international students
- Researcher Database
- Entrance Exam
- Tuition Fees
- International Student Support (for new students)
-
Support for international students (for current students)
- Scholarships for International Students
- Japanese Language Course for International Students
- Immigration procedures (renewal of period of stay, permission to engage in activities other than those permitted under the status of residence, re-entry permission)
- Procedures after arriving in Japan
- Procedures for changing address (under construction)
- Procedures upon returning to Japan
- Notification of absence due to temporary return to Japan, travel, etc.
- Employment for international students
- Emergency Contact Information
- Studying abroad from Muro Institute of Technology
- Request for donations
- HOME
- Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
- Faculty of Science and Engineering
- Department of System Science and Chemistry
- Mathematical Information Systems Course
Mathematical Information Systems Course

I want to create the next generation of software! I want to use informatics to solve social problems!
Students will study science that explores the essence of problems ranging from elucidating natural phenomena to understanding local problems from the perspective of mathematical information systems. In particular, students will study a wide range of information science based on mathematics, which provides a logical foundation, and conduct education and research that combines information-related science and engineering.
About the Education Program
Cultivate high-level information processing skills while learning the fundamentals of information science through practical experience
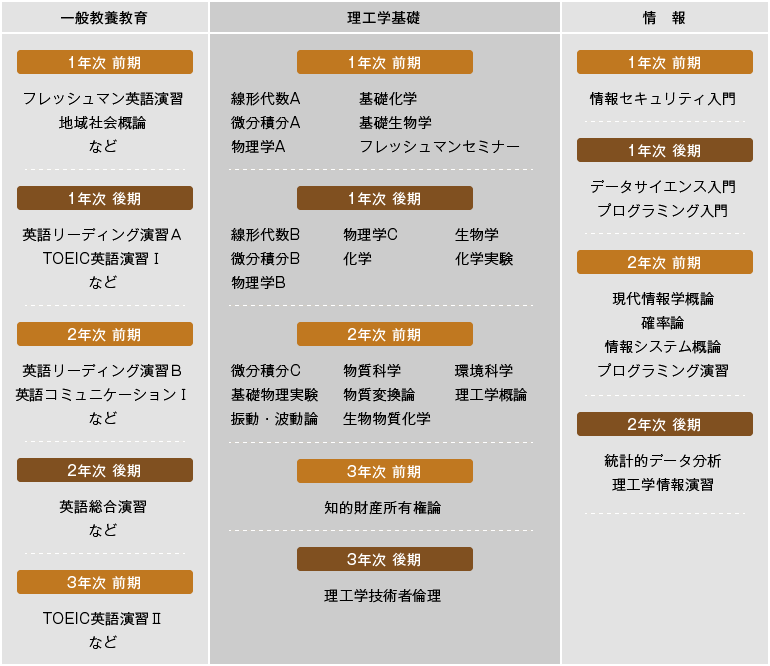
From the first year to the first half of the second year, students take general education subjects, faculty and department common subjects (natural sciences) and some information subjects. Through these, students will acquire communication skills and social literacy, as well as a wide range of knowledge on natural sciences (mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology) and basic knowledge on information science. From the second half of the second year onwards, this course divides its subjects into informatics, the study of the principles and technology of handling large amounts of information in nature and society, mathematics, which is its foundation, mathematics and information/society, information fundamentals, information systems, and programming, and also includes practical exercises, and students systematically take subjects in each field. Furthermore, by studying informatics comprehensively, students will develop the ability to abstractly and logically organize and analyze large amounts of data.
Mathematical Information Systems Course

Flow of the four years
First year
General education subjects include subjects related to people and society, foreign languages, regional collaboration subjects, common natural science subjects including mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology, and information-related subjects including information security, data science, and programming.
Second Year
Students will learn about natural sciences across disciplines through subjects such as "Material Transformation Theory," "Biomaterial Chemistry," "Vibration and Wave Theory," and "Material Science," and will also learn about information science through subjects such as "Introduction to Modern Informatics," "Probability Theory," "Statistical Data Analysis," and "Introduction to Information Systems." From the second semester, students will begin taking specialized subjects in each course.
Third Year
Continuing from the second semester of the second year, students will study specialized course subjects. They will take subjects such as "algebra," "geometry," "analysis," "signal processing," "information theory," and "programming" to acquire a wide range of specialized knowledge related to the field, and will also carry out exercises ranging from basic to applied science to integrate and utilize these knowledge.
Fourth Year
The main part of learning in the fourth year is practical, through graduation research. By applying the knowledge acquired up to that point to problems set in each field, students will make their knowledge more essential and develop their problem-solving skills.
Mathematical Information Systems Course Pickup
About the classes
Informatics PBL Seminar
By carrying out practical exercises (PBL, Problem Based Learning) in which students develop software to solve given problems, students will develop problem-solving skills while independently preparing, researching, learning, and discussing. Students will form groups, determine on their own what is needed to develop the software for the problem, gather materials, study on their own, and work together as a group to accomplish the problem.

About the Research
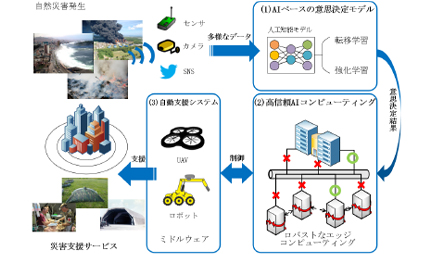
Research and development of more practical disaster response systems using cutting-edge technology
Since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011, industry, academia and government have been working together to tackle the issue of disaster resistance. ICT is expected to be used in the field of disaster resistance, but existing ICT is mainly used for data management and information transmission, and its benefits have not been fully utilized. Therefore, we aim to apply cutting-edge AI and communication technologies to research and develop more practical disaster-resistant systems. Specifically, after a disaster occurs, a wide variety of data collected from sensors and cameras is analyzed to accurately grasp the damage situation and make quick decisions such as rescue. In addition, by performing tasks without being affected by damage to network infrastructure, it becomes possible to automatically control robots, drones, etc. based on the results of calculations by AI.

Professor Dong Mian-Hsiung
Research Field
Information Network
Main research themes
Building a disaster-resistant system using ICT technology
Licenses and qualifications available
driver licence
- High school teacher's license (mathematics), etc. *Requires completion of teaching course credits
Employment situation
- iD
- Accenture
- Alpha Systems
- SEC
- NTT Data MSE
- NTT Data Hokkaido
- OKI Software
- Keyware Solutions
- KDDI
- SoftCreate Holdings
- Communication
- Tsuuken Advanced Systems
- DNP Information Systems
- Techno Lab
- Dwell
- Tohokushinsha
- Panasonic ITS
- Hitachi Information and Communication Engineering
- B.U.G. DGM Mori Seiki
- PFU
- Nippon Steel Tex Engineering
- IBM Japan Solution Services
- NEC
- Akie
- Hokkaido NS Solutions
- Hokkaido Electric Power
- Meitec
- Mobitech
- Ricoh IT Solutions
- Civil servant (Hokkaido)
- High school teacher (Hokkaido)
- Graduate school (Muroran Institute of Technology, Hokkaido University, etc.)


