-
University Guide
 University Guide
University Guide
INDEX- Introducing the President
- University Introduction
- University Evaluation
-
Policies and Initiatives
- Policy and Initiatives INDEX
- Compliance
- Crisis Management System
- Promoting gender equality
- International Exchange Policy
- Infrastructure longevity plan (individual construction plan)
- Environmental Initiatives
- Smoking is prohibited throughout the university grounds.
- Safety Management Action Plan
- JABEE Initiatives
- Basic rules regarding drinking among Muroran Institute of Technology students
- Policy for promoting the sharing of research facilities and equipment at Muroran Institute of Technology
- Campus Master Plan
- Muroran Institute of Technology Conflict of Interest Management Policy
- Digital Campus Promotion
- Muroran Institute of Technology Open Access Policy
- Muroran Institute of Technology Research Data Policy
-
Information Disclosure
- Information Disclosure INDEX
- Disclosure of corporate information (information about the organization)
- Disclosure of corporate information (information regarding business)
- Disclosure of corporate information (financial information)
- Publication of corporate information (evaluation information)
- Disclosure of corporate information (audit information)
- Publication of educational information
- Compliance status with the National University Corporation Governance Code
- Rules
- Information Disclosure System
- Personal Information Protection System
- Publication of guidelines for employees regarding the promotion of the elimination of discrimination against people with disabilities
- Announcement of the New Support System for Higher Education
- Application and recruitment information
- public relations
-
Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
 Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
INDEX- Faculty of Science and Engineering
- graduate school
-
Affiliated facilities (centers, etc.)
- Affiliated Facilities (Centers, etc.) INDEX
- Creative Collaboration Center
- Aerospace Plane Research Center
- Rare Earth Materials Research Center
- Computer Science Center
- Research Infrastructure Equipment Sharing Center
- Technology Department
- Career Support Center
- International Exchange Center
- Information Education Center
- Affiliated Library
- Health Management Center
- Gender Equality Promotion Office
- MONO Creation Future Co-Creation Organization
- Regional Collaboration Human Resources Development Center
- Manufacturing Infrastructure Center
- Robot Arena
- satellite
- Tokyo Office
- the study
-
Student Life/Employment
 Student Life/Employment
Student Life/Employment
INDEX-
Courses and classes
- Course/Class INDEX
- Academic Calendar
- Lesson plan (syllabus)
- Classes (timetable)
- Exam (timetable)
- Course Affiliation
- Credit transfer with other universities
- Re-reading of course subjects
- CAMPUS SQUARE (Course registration)
- How to take the course
- Student Handbook/Graduate School Course Guidelines
- Transfer of departments, etc.
- Doctoral Degree Application Guide
- Academic Counseling and Guidance
- Duration of study
- Long-term student system
- Educational Programs (not required for graduation or completion)
- A Note About Generative AI
-
Student Life
- Student Life INDEX
- Suspension and Absence
- Various notification and certificate issuance procedures
- Student ID and student number
- Student discount card/school attendance certificate
- Procedures for taking a leave of absence, reinstating, and withdrawing from school
- New academic year orientation
- Preserving the on-site environment
- Attention students
- Transportation on and off campus
- Message board/contact method
- Harassment
- health care
- Events
- Welfare facilities
- Student Dormitory
- Student Support Center Introduction
- Student General Advice Office
- Extracurricular Activities
- Tuition, scholarships and other procedures
- Employment and qualification support
-
Courses and classes
-
Entrance Examination Information
 Entrance Examination Information
Entrance Examination Information
INDEX- University Entrance Examination [Faculty]
- Graduate School Entrance Examination
- Transfer Admissions
- Entrance examination for international students
- Specialized students and research students
- Admission procedures, tuition fees, etc.
- FAQ
- University Introduction
- Request information

-
Social Cooperation
 Social Cooperation
Social Cooperation
INDEX- Collaborative News
- Collaboration Centers, etc.
-
Industry-academia-government collaboration
- Industry-academia-government collaboration INDEX
- Alliance Lab
- Research Collaboration Association
- Muro Institute of Technology venture title
- Confidentiality
- Joint Research System
- Commissioned Research System
- Academic Guidance System
- Tangible research results
- Scholarship and Donation System
- Donation field etc.
- Future Creation Promotion Expenses
- Regarding the expenditure of personnel expenses of the principal investigator (PI) from direct costs of competitive research grants
- Research ethics and safety
- Public Lectures
- Muro Institute of Technology Science School
- University Visit
- Robot Soccer Contest
- Re-education for working adults
-
International Exchange
 International Exchange
International Exchange
INDEX- International Academic Exchange Agreements
- Number of international students
- Researcher Database
- Entrance Exam
- Tuition Fees
- International Student Support (for new students)
-
Support for international students (for current students)
- Scholarships for International Students
- Japanese Language Course for International Students
- Immigration procedures (renewal of period of stay, permission to engage in activities other than those permitted under the status of residence, re-entry permission)
- Procedures after arriving in Japan
- Procedures for changing address (under construction)
- Procedures upon returning to Japan
- Notification of absence due to temporary return to Japan, travel, etc.
- Employment for international students
- Emergency Contact Information
- Studying abroad from Muro Institute of Technology
- Request for donations
-
University Guide
University Guide INDEX
- Introducing the President
- University Introduction
- University Evaluation
-
Policies and Initiatives
- Policy and Initiatives INDEX
- Compliance
- Crisis Management System
- Promoting gender equality
- International Exchange Policy
- Infrastructure longevity plan (individual construction plan)
- Environmental Initiatives
- Smoking is prohibited throughout the university grounds.
- Safety Management Action Plan
- JABEE Initiatives
- Basic rules regarding drinking among Muroran Institute of Technology students
- Policy for promoting the sharing of research facilities and equipment at Muroran Institute of Technology
- Campus Master Plan
- Muroran Institute of Technology Conflict of Interest Management Policy
- Digital Campus Promotion
- Muroran Institute of Technology Open Access Policy
- Muroran Institute of Technology Research Data Policy
-
Information Disclosure
- Information Disclosure INDEX
- Disclosure of corporate information (information about the organization)
- Disclosure of corporate information (information regarding business)
- Disclosure of corporate information (financial information)
- Publication of corporate information (evaluation information)
- Disclosure of corporate information (audit information)
- Publication of educational information
- Compliance status with the National University Corporation Governance Code
- Rules
- Information Disclosure System
- Personal Information Protection System
- Publication of guidelines for employees regarding the promotion of the elimination of discrimination against people with disabilities
- Announcement of the New Support System for Higher Education
- Application and recruitment information
- public relations
-
Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc. INDEX
- Faculty of Science and Engineering
- graduate school
-
Affiliated facilities (centers, etc.)
- Affiliated Facilities (Centers, etc.) INDEX
- Creative Collaboration Center
- Aerospace Plane Research Center
- Rare Earth Materials Research Center
- Computer Science Center
- Research Infrastructure Equipment Sharing Center
- Technology Department
- Career Support Center
- International Exchange Center
- Information Education Center
- Affiliated Library
- Health Management Center
- Gender Equality Promotion Office
- MONO Creation Future Co-Creation Organization
- Regional Collaboration Human Resources Development Center
- Manufacturing Infrastructure Center
- Robot Arena
- satellite
- Tokyo Office
- the study
-
Student Life/Employment
Student Life/Employment INDEX
-
Courses and classes
- Course/Class INDEX
- Academic Calendar
- Lesson plan (syllabus)
- Classes (timetable)
- Exam (timetable)
- Course Affiliation
- Credit transfer with other universities
- Re-reading of course subjects
- CAMPUS SQUARE (Course registration)
- How to take the course
- Student Handbook/Graduate School Course Guidelines
- Transfer of departments, etc.
- Doctoral Degree Application Guide
- Academic Counseling and Guidance
- Duration of study
- Long-term student system
- Educational Programs (not required for graduation or completion)
- A Note About Generative AI
-
Student Life
- Student Life INDEX
- Suspension and Absence
- Various notification and certificate issuance procedures
- Student ID and student number
- Student discount card/school attendance certificate
- Procedures for taking a leave of absence, reinstating, and withdrawing from school
- New academic year orientation
- Preserving the on-site environment
- Attention students
- Transportation on and off campus
- Message board/contact method
- Harassment
- health care
- Events
- Welfare facilities
- Student Dormitory
- Student Support Center Introduction
- Student General Advice Office
- Extracurricular Activities
- Tuition, scholarships and other procedures
- Employment and qualification support
-
Courses and classes
- Entrance Examination Information
-
Social Cooperation
Social Collaboration INDEX
- Collaborative News
- Collaboration Centers, etc.
-
Industry-academia-government collaboration
- Industry-academia-government collaboration INDEX
- Alliance Lab
- Research Collaboration Association
- Muro Institute of Technology venture title
- Confidentiality
- Joint Research System
- Commissioned Research System
- Academic Guidance System
- Tangible research results
- Scholarship and Donation System
- Donation field etc.
- Future Creation Promotion Expenses
- Regarding the expenditure of personnel expenses of the principal investigator (PI) from direct costs of competitive research grants
- Research ethics and safety
- Public Lectures
- Muro Institute of Technology Science School
- University Visit
- Robot Soccer Contest
- Re-education for working adults
-
International Exchange
International Exchange Index
- International Academic Exchange Agreements
- Number of international students
- Researcher Database
- Entrance Exam
- Tuition Fees
- International Student Support (for new students)
-
Support for international students (for current students)
- Scholarships for International Students
- Japanese Language Course for International Students
- Immigration procedures (renewal of period of stay, permission to engage in activities other than those permitted under the status of residence, re-entry permission)
- Procedures after arriving in Japan
- Procedures for changing address (under construction)
- Procedures upon returning to Japan
- Notification of absence due to temporary return to Japan, travel, etc.
- Employment for international students
- Emergency Contact Information
- Studying abroad from Muro Institute of Technology
- Request for donations
- HOME
- Faculty/Graduate School/Center etc.
- Faculty of Science and Engineering
- Department of Creative Engineering
- Electrical and Electronic Engineering Course
Electrical and Electronic Engineering Course

I want to think about technology that makes things autonomous! I want to learn about electricity that supports society!
We provide education and research that spans the fundamentals to applications of electrical and electronic engineering, communications engineering, and measurement and control engineering, including the technology for generating and sending electricity to homes and factories, the electronic circuits used in computers and home appliances, materials such as semiconductors used in electronic components, the communications technology that supports the Internet, and the motors that power robots.
About the Education Program
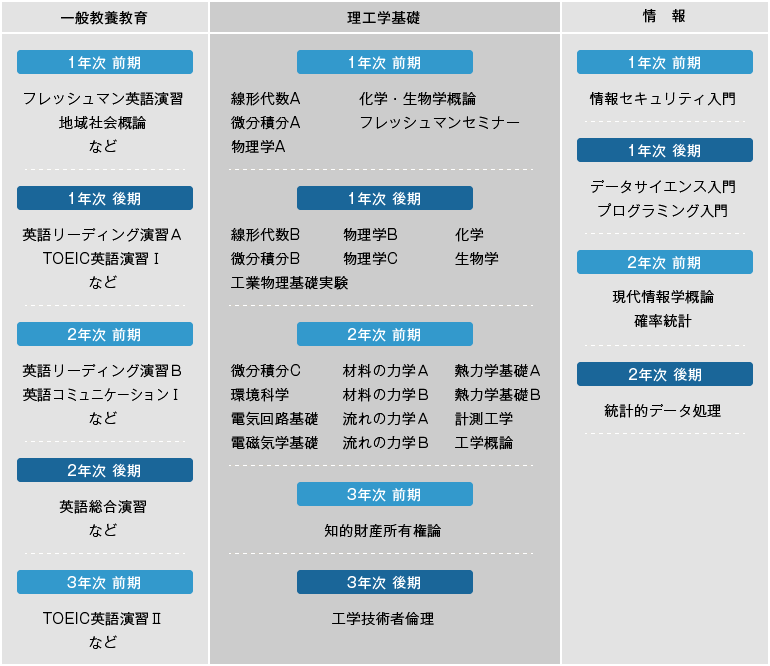
In addition to general education, students will systematically study specialized fields of electronics.
From the first to the first half of the second year, students take general education subjects, faculty and department common subjects (natural sciences) and some information subjects to acquire communication skills and social literacy, as well as basic specialized subjects in related fields (material mechanics, fluid mechanics, measurement engineering, etc.) to develop a broad perspective. From the second half of the second year onwards, students in this course systematically study specialized curricula related to electrical and electronic engineering, communication engineering, and measurement and control engineering, with a focus on electrical energy, measurement and communication, electronic physical properties devices, and engineering design and experiments.
Electrical and Electronic Engineering Course

Flow of the four years
First year
Students will develop the fundamentals of science and engineering by studying general education subjects such as "human and society-related subjects," "foreign language subjects," and "regional collaboration subjects," common natural science subjects such as "mathematics," "physics," "chemistry," and "biology," and information-related subjects such as "Introduction to information security," "Introduction to data science," and "Introduction to programming."
Second Year
In the first semester, students will study a range of subjects across fields, including "Basics of Electromagnetism," "Basics of Electrical Circuits," "Mechanics of Materials," "Mechanics of Flow," "Basics of Thermodynamics," and "Measurement Engineering," to improve their basic engineering skills. In addition, students will acquire data utilization skills through information subjects such as "Introduction to Modern Informatics," "Probability and Statistics," and "Statistical Data Processing." In the second semester, students will study basic course-specific subjects such as "Electromagnetism," "Digital Circuits," and "Electronic Properties."
Third Year
From the second semester of the second year, students continue to study course-specific subjects. Students study required subjects such as "Semiconductor Engineering," "Control Engineering," and "Electrical and Electronic Engineering Experiments," as well as elective subjects such as "Communications Engineering," "Power Transmission and Distribution Engineering," and "Electrical and Electronic Materials," acquiring specialized knowledge that is the foundation of electrical and electronic engineering, communications engineering, and measurement and control engineering, and acquiring applied skills through practical training.
Fourth Year
The main part of learning in the fourth year is practical, through graduation research. By applying the knowledge acquired up to that point to problems set in each field, students will make their knowledge essential and develop their problem-solving skills.
Electrical and Electronic Engineering Course Pickup
About the classes
Electrical and Electronic Engineering Experiments A and B

Students will deepen their understanding of the basic subjects of electrical engineering and electronics by confirming the basic laws and characteristics of electrical measurement, control, communication, power, high voltage, electrical equipment, and optoelectronics that they have learned up to the third year through actual experiments. Through this course, students will also learn the operating principles and operation methods of basic measuring equipment. In this photo, the characteristics of a motor and a generator are being investigated. After confirming the method, students will work together to carry out the experiment.
About the Research
Development of a four-legged running robot with elastic legs
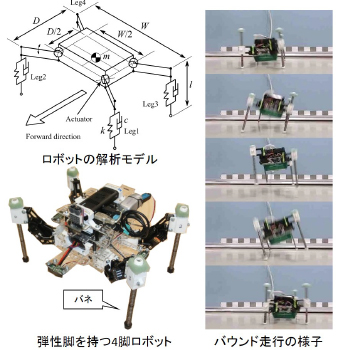
By utilizing the frequency entrainment phenomenon of nonlinear oscillators, it is possible to synchronize multiple systems that are vibrating independently. In this research, we have developed a four-legged robot with springs attached to the legs as shown in the figure, and aim to achieve high-speed running by utilizing the vibration of the springs. By appropriately synchronizing the leg motion and spring vibration using the frequency entrainment phenomenon, the elastic energy of the spring can be efficiently amplified, and efficient running can be expected by utilizing this elastic energy. Currently, with this robot, hopping motion and bounding running in all directions can be achieved by appropriately synchronizing the motion of each leg with the vibration of the springs and changing the synchronization timing of the four legs.

Professor Shuichi Kajiwara
Research Field
Control Engineering, Mechatronics, Robotics
Main research themes
Control of mechanical systems using entrainment of nonlinear oscillators
Licenses and qualifications available
driver licence
- High school teacher's license (industrial) etc. *Teacher training course credits required
Qualifications
- Chief Electrical Engineer (requires a certain amount of practical experience after graduation)
- Radio operator
- Telecommunications Chief Engineer (requires a certain amount of work experience after graduation)
- Assistant Engineer, etc.
Employment situation
- NEC
- Oki Electric Industry
- Power Development
- Nipro
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Japan Radio
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- National Police Agency Hokkaido Police Information and Communications Department
- sharp
- MinebeaMitsumi
- Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
- FANUC
- Nippon Chemi-Con
- Nippon Steel Tex Engineering
- Hokkaido Railway Company
- Nippon Signal
- NTT East Group Company
- Yotsuba Milk Industry
- Mitsubishi Electric Plant Engineering
- Japan Nuclear Fuel
- Hokkaido Electric Power
- PFU
- Toyota Motor Hokkaido
- Sapporo City Hall (Electrical Worker)
- Nippon Paper Industries
- Kobelco Construction Machinery
- Kawaju Gifu Engineering
- Obayashi Corporation
- Central Engineering
- Churyo Engineering
- Tokyo Fire Department
- Nippon Express
- Japanese Airplane
- Hitachi Automotive Systems
- Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems
- Hitachi Zosen
- Ryoyu Systems, etc.


