Architecture and Civil Engineering Course

I want to think about technology to prevent natural disasters! I want to learn how to create a comfortable living environment!
We provide education and research that covers everything from the fundamentals to applications of architecture and civil engineering, including buildings such as houses and other buildings, civil structures such as roads, bridges, and tunnels, the living spaces in which we live, the urban planning that supports our lives, and disaster-resistant town planning.
About the Education Program
Acquire general knowledge and basic skills to move on to the specialized fields of "Architecture" and "Civil Engineering"
From the first year through the first semester of the second year, students take general education subjects, faculty and department-wide (natural science) subjects, and some information-related subjects to acquire communication skills and social literacy, while also learning specialized foundational subjects in related fields (material mechanics, electrical circuits, measurement engineering, etc.) to develop an overall perspective.
In the first half of the second semester of the second year, students study general subjects for this course, and in the second half they split into two tracks, architecture and civil engineering, to study specialized subjects in each track.
Architecture Track
Students will systematically study subjects related to design and planning, environment and production, structure, and practice, with a focus on the designated subjects for the architect examination.

Civil Engineering Track
Students will systematically study subjects in the fields of geotechnical, structural and material, hydraulic, planning and transportation, sanitation, and practical work, with a focus on civil engineering subjects required for design and construction management.
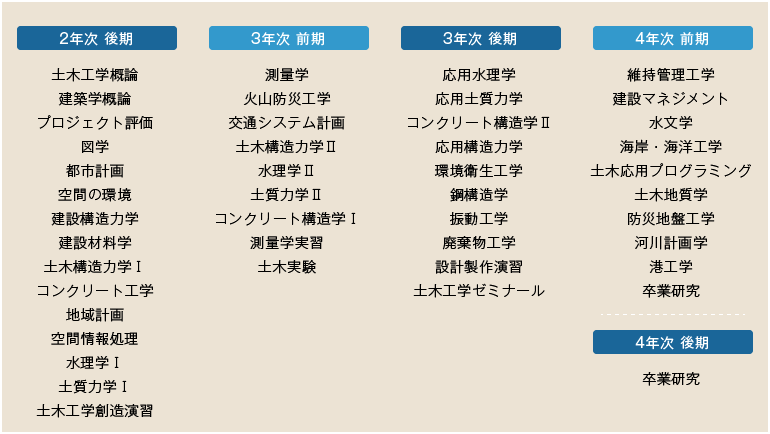
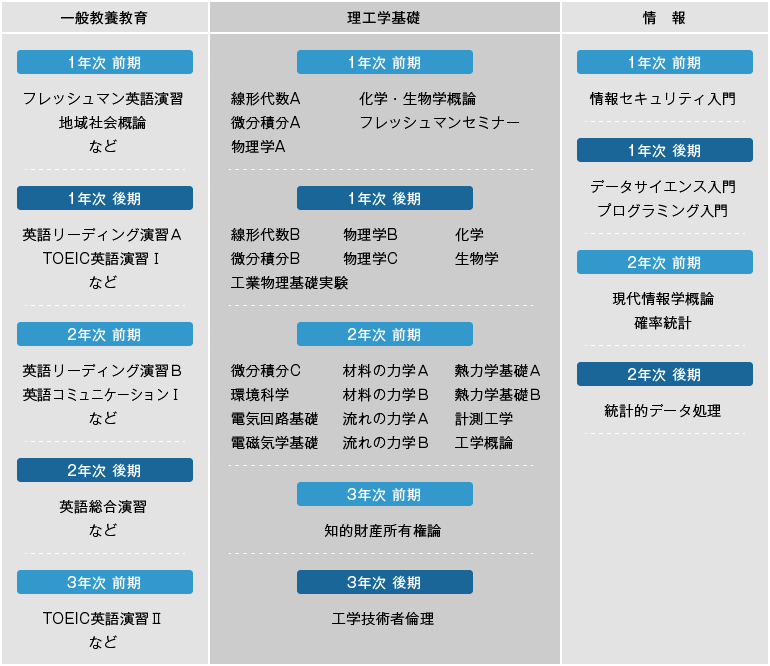
Flow of the four years
First year
Students will develop the fundamentals of science and engineering by studying general education subjects such as "human and society-related subjects," "foreign language subjects," and "regional collaboration subjects," common natural science subjects such as "mathematics," "physics," "chemistry," and "biology," and information-related subjects such as "Introduction to information security," "Introduction to data science," and "Introduction to programming."
2nd year first semester
In the first semester, students will study a range of subjects across fields, including "Fundamentals of Electromagnetism," "Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits," "Mechanics of Materials," "Mechanics of Flow," "Fundamentals of Thermodynamics," and "Measurement Engineering," to improve their basic engineering skills.
Furthermore, students will acquire the ability to utilize data through information subjects such as "Introduction to Modern Informatics," "Probability and Statistics," and "Statistical Data Processing."
Second Year, Second Semester
From the second semester onwards, students will focus on track-specific subjects. In the first half of the second semester, students will study track-wide subjects and introductory subjects such as "Descriptor Drawing," "Urban Planning," and "Structural Mechanics for Construction," and from the second half of the second semester, students will study specialized subjects for each track.
The architecture track includes basic specialized subjects such as "Basics of Architectural Design," "Urban and Regional Planning," and "Architectural Exercises," while the civil engineering track includes basic specialized subjects such as "Spatial Information Processing," "Hydraulics," and "Soil Mechanics."
Third Year
From the second semester of the second year, students will continue to focus on specialized track subjects.
The Architecture Track offers compulsory courses such as "Architectural Design Theory," "Architectural Equipment," and "Architectural Reinforced Concrete Structure," as well as elective courses such as "Urban Management," "Cold Climate Architectural Environmental Engineering," and "Architectural Surveying Practice."
In the civil engineering track, students study required subjects such as "Transportation System Planning," "Volcanic Disaster Prevention Engineering," and "Surveying Practice," as well as elective subjects such as "River Planning," "Environmental Sanitation Engineering," and "Coastal and Marine Engineering." Through these courses, students will acquire specialized knowledge that is the core of each field and develop the ability to apply that knowledge through practical training.
Fourth Year
The main part of learning in the fourth year is practical learning through graduation research. By applying the knowledge acquired up to that point to achieve the tasks set in each field, students will develop problem-solving skills as well as an essential understanding of the knowledge.
Architecture Truck Pickup
About the classes
Architectural Design I (second year second semester)
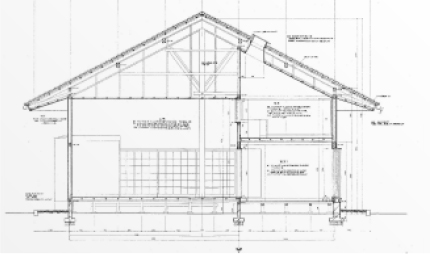
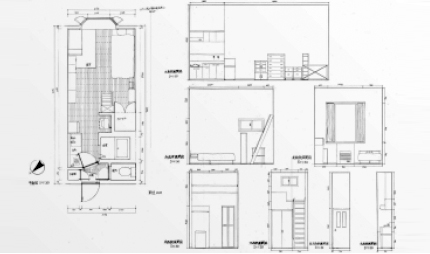
This is a practical course to learn drawing techniques, which are the basis of architectural design. Students will learn "basic expressions and rules for various architectural drawings (floor plans, elevations, etc.)" and "how to use drawing tools." In practice, students will create drawings based on actual measurements of their own rooms, and copy and trace drawings of existing houses (wooden) and public buildings (reinforced concrete structure).
About the Research
Research on childcare support services in urban parks in response to the declining population

In recent years, as socio-economic conditions have changed, such as a rapid decline in population and an aging society, there is a demand for new value to be created in architecture and urban development in response to these changes.
Up until now, city parks have been developed and stocked with a park area per person of 10 m2/person, and the total area across the country is roughly the same as that of the main island of Okinawa (120,000 ha), but city parks are also in a situation where new value needs to be created.In this situation, childcare support services in new city parks are attracting attention as a way to deal with the declining population.
This study will examine the current state of child-rearing support services in urban parks, the increase in park usage resulting from the implementation of child-rearing support services, the possibility of human resource development through these services, and park management strategies for this purpose.

Professor Tsuneshi Ichimura
Research Field
Landscape, Urban Management, Environmental Planning
Main research themes
New business and management in urban parks to solve local issues
Civil Engineering Truck Pickup
About the classes
Civil Engineering Experiment
In order to understand the properties of "soil," "reinforced concrete," and "water," which are important for the design and construction of civil engineering structures such as roads, bridges, rivers, and harbors, students will conduct standard soil tests, reinforced concrete experiments, and hydraulic experiments that are used in practice. Students will learn how to understand the properties of "soil," "reinforced concrete," and "water" based on the results of these experiments, deepening their understanding of the theories and knowledge they learned in lectures. This class also develops communication skills through group work.


About the Research
Predicting water risks caused by global climate change and preparing for disasters

In recent years, there have been frequent disasters caused by "guerilla downpours" where heavy rain falls in a short period of time and unprecedented heavy rain. At the same time, there are concerns about the decrease in snowfall and its sudden melting. The most commonly heard cause is global climate change.
Predicting such risks related to water will lead to disaster prevention measures and protect our safety. In this research, we use models like the one in the photo and simulation technology to investigate the water and sediment phenomena that occur during floods, and consider what countermeasures we can take. We also explore the mechanisms of the water cycle throughout the basin, including precipitation, snowmelt, evapotranspiration, and runoff, and consider the impact of climate change on water use and the water environment, as well as countermeasures.

Professor Makoto Nakatsugawa
Research Field
Hydrology, river engineering, water environment engineering
Main research themes
Impacts of climate change on floods, water resources and the water environment, and adaptation measures; flood forecasting; natural restoration of rivers and wetlands
Licenses and qualifications available
driver licence
- High school teacher license (industrial) *Teacher training course credits required
Qualifications
- Qualification to take the first-class architect examination (requires a certain amount of work experience after graduation)
- Qualifications for taking the second-class architect exam
- 1st and 2nd class construction management engineers (requires a certain amount of work experience after graduation)
- Surveyor
- Assistant Engineer, etc.
Employment situation
Architecture Track
- Obayashi Corporation
- Shimizu Corporation
- Kajima Construction
- Taisei Corporation
- Takenaka Corporation
- Toda Construction
- Kumagai Gumi
- Nishimatsu Construction
- Fujita
- Iwata Chizaki Construction
- Ito Construction
- Daiwa House Industry
- Dokon
- Hokkaido
- Muroran Institute of Technology Graduate School, etc.
Civil Engineering Track
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism Hokkaido Regional Development Bureau
- Hokkaido
- Toyama Prefecture
- Sapporo City
- Hakodate City
- Kajima Construction
- Obayashi Corporation
- Taisei Corporation
- Nishimatsu Construction
- Dokon
- Nippon Koei
- Yachiyo Engineering
- Hokkaido Electric Power
- Hokkaido Railway Company
- Muroran Institute of Technology Graduate School, etc.